

5TH METATARSAL FRACTURE IN CHILD FULL
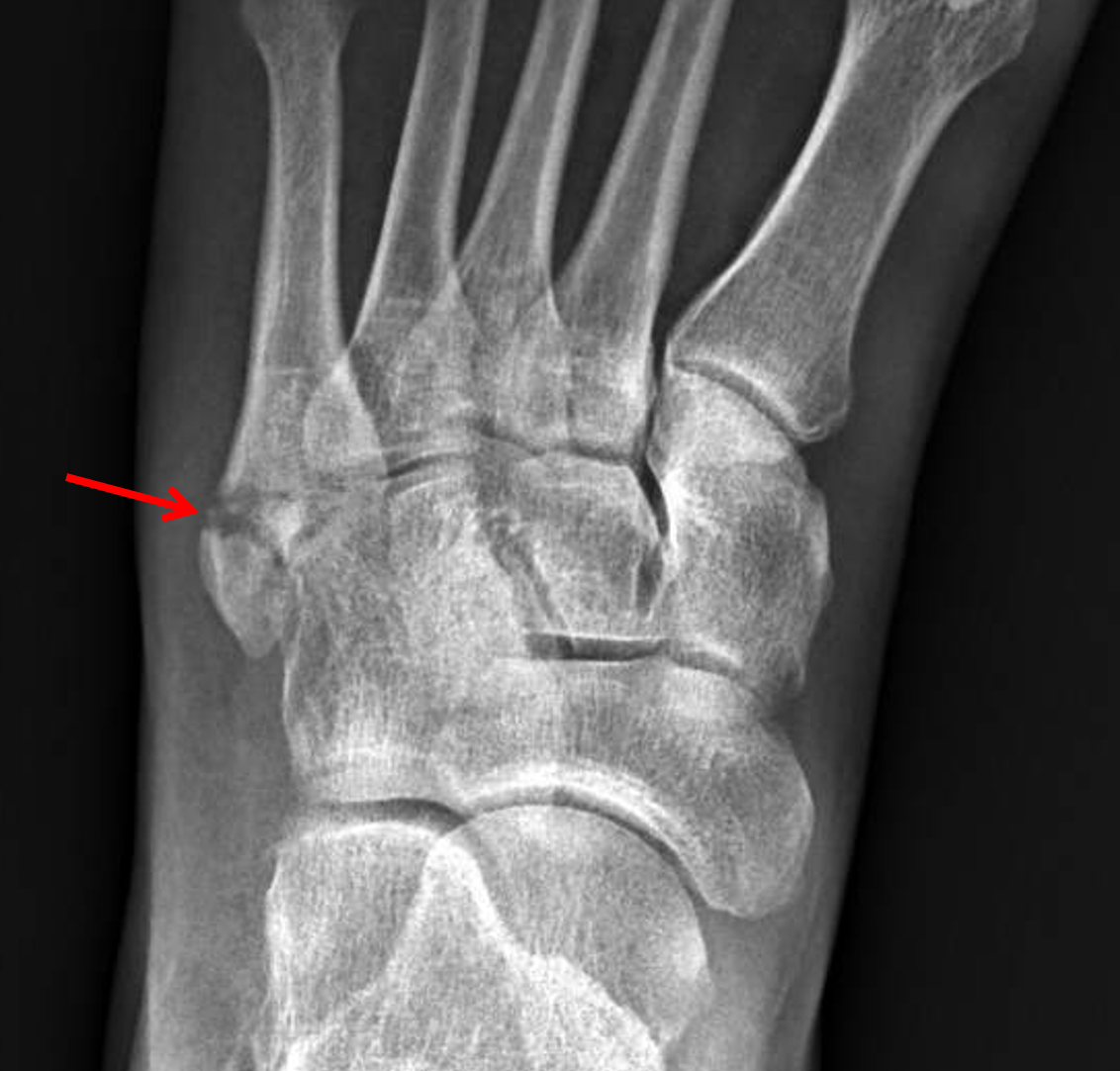
The term “early functional conservative therapy” involves immediate full weight-bearing as tolerated without immobilization.Įvaluation of the studies was performed using the “Methodological index for non-randomized studies” score (MINORS score) ( 7). This classification distinguishes between three fracture types, depending on the fracture pattern in relation to the base of the 4th–5th intermetatarsal articulation: Zone 1 – proximal to the intermetatarsal articulation, Zone 2 – in the region of the articulation, Zone 3 – at the distal end of the articulation ( Figure 2a). The study parameters are presented in etable 2.Īnalysis of the papers included was made based on the fracture location classification according to Lawrence and Botte ( 3). The assessment of the study quality and data extraction were also conducted by the two independent examiners (VH, HP) using Microsoft Excel (Version 16.46, Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, Washington, USA). Any disagreements were finally decided by an independent third examiner (SB).
5TH METATARSAL FRACTURE IN CHILD SOFTWARE
The management and implementation of the systematic literature search was conducted using Covidence systematic review software (Veritas Health Innovation, Melbourne, Australia The relevant articles were identified in a stepwise fashion, first of all based on titles and abstracts, then on the full texts, in each case by two independent investigators (VH, HP). The study protocol was prospectively registered in PROSPERO (CRD 42020185294, 5 July 2020). The inclusion criteria in terms of the PICOS framework ( 13) are presented in etable 1. Exclusion criterion was the presence of other injuries, apart from a fracture of the base of MT5 on the contralateral side. Also analyzed were randomized cohort studies (RCT) or comparative cohort studies which either examined the same treatment for different fracture types (according to Lawrence and Botte) or different forms of treatment for the same fracture type of the base of MT5. Where a study used a different term, it was „translated“ into the Lawrence and Botte classification. The Lawrence and Botte ( 3) classification was used for the analysis. The classification used had no effect on the study selection. (“fifth metatarsal*”:ti,ab,kw OR “5th metatarsal*”:ti,ab,kw OR “MT V”:ti,ab,kw OR “Jones”: ti,ab,kw OR “Lawrence”: ti,ab,kw OR MeSH descriptor: ) AND “fracture*”:ti,ab,kw OR MeSH descriptor: ) TITLE-ABS-KEY (“fifth metatarsal*” OR “5th metatarsal*” OR “MT V” OR “Jones” OR “Lawrence”) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY (“fracture*”) (‘fifth metatarsal*’:ti,ab OR ‘5th metatarsal*’:ti,ab OR ‘MT V‘:ti,ab OR ‘jones’:ti,ab OR ‘Lawrence’:ti,ab) AND (‘fracture*’:ti,ab OR exp Fracture) (TI “fifth metatarsal*” OR AB “fifth metatarsal*” OR TI “5th metatarsal*” OR AB “5th metatarsal*” OR TI “MT V” OR AB “MT V” OR TI “Jones” OR AB “Jones” OR TI “Lawrence” OR AB “Lawrence” OR (MH “Metatarsal Fractures”))ĪND (TI “fracture*” OR AB “fracture*” OR (MH “Fractures”)) (“fifth metatarsal*” OR “5th metatarsal*” OR “MT V” OR “Jones” OR “Lawrence” OR “Metatarsal Bones/injuries” ) AND (“fracture*” OR “Fractures, Bone”)
The complete search strategies for all databases are shown below. In addition, a search for „grey literature“ in the form of conference papers was carried out in both Scopus and EMBASE, as well as a hand search in the references of included studies and reviews on the topic. The systematic literature search was conducted according to the PRISMA statement (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses) ( 12) in the databases MEDLINE (PubMed), CINAHL, Scopus, EMBASE, CENTRAL from database inceptions until 5.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
